Spectrum plots¶
Spectrum plots label their axes as F and Y. It defaults to a log-log plot the most common if not
standard presentation in LIGO. To manually set the limits of the plot use --fmin and --fmax
for the frequency axis and --ymin and --ymax for the Amplitude axis. If any are left blank
they are set to the min or max of the data.
If you prefer linear axes use the --nologf and --nology parameters. This can be useful
to zoom in on peaks and lines in the spectrum.
The spectrum presented is an average of multiple FFTs controled by --secpfft and --overlap.
--secpfft specifies the length of the FFT in seconds (not limited to powers of 2 or integers)
and --overlap specifies a fractional overlap for the next FFT. For example a 1 second FFT of a
100 Hz channel with an overlap of 0.1 would generate the first FFT with samples 0-99 and the second
FFT with samples 10-109. More overlap results in more averaging and a higher SNR. Longer FFTs
result in better frequency resolution and less “frequency bleed”.
For example the following command line produces a fairly high frequency resolution plot of OAF-CAL_DARM from the 2014-02-14 lock at LLO:
gwpy-plot spectrum --chan L1:OAF-CAL_DARM_DQ --start 1107936067 --duration 120 --secpfft 10
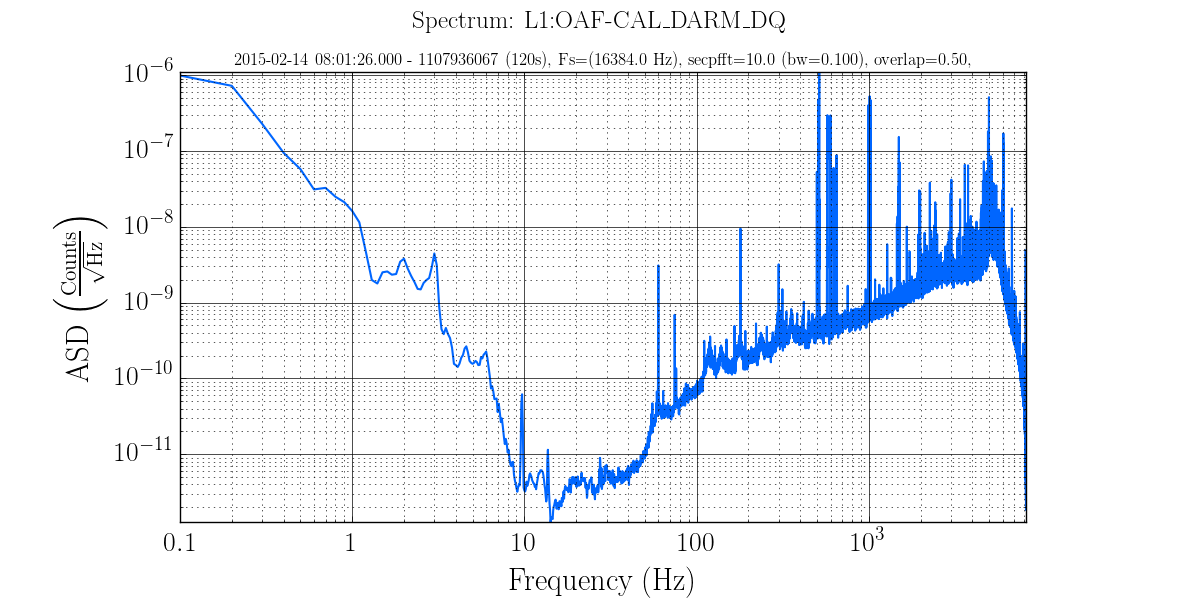
To zoom in on the lines between 500 and 700 Hz we could use the following:
gwpy-plot spectrum --chan L1:OAF-CAL_DARM_DQ --start 1107936067 --duration 120 \
--secpfft 10.000 --overlap 0.90 --nologf --fmin 500 --fmax 700
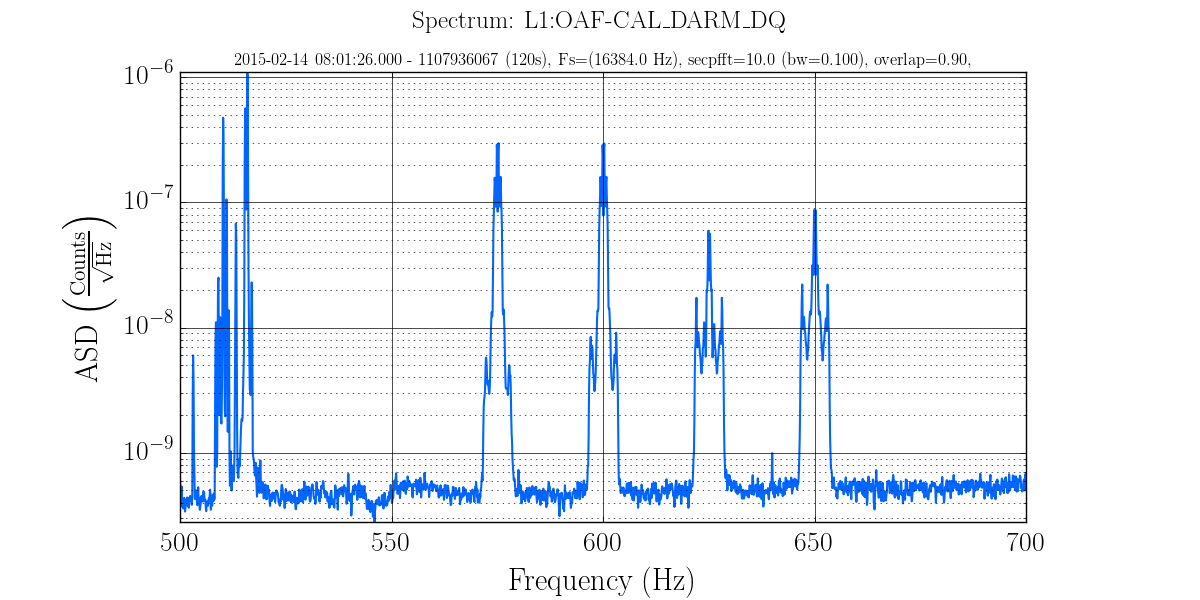
Because the question such a plot could answer is exactly where are the lines, we use a linear frequency axis. Longer FFTs and a smaller frequency range would produce more resolution.
The full help text for the Spectrum plot product is:
$ gwpy-plot spectrum --help
usage: gwpy_ldvw spectrum [-h] [-v] [-s SILENT] --chan CHAN [CHAN ...] --start
START [START ...] [--duration DURATION]
[-c FRAMECACHE] [--highpass HIGHPASS]
[--secpfft SECPFFT] [--overlap OVERLAP] [--nologf]
[--fmin FMIN] [--fmax FMAX] [--nology] [--ymin YMIN]
[--ymax YMAX] [-g GEOMETRY] [--interactive]
[--title TITLE] [--suptitle SUPTITLE]
[--xlabel XLABEL] [--ylabel YLABEL] [--out OUT]
[--legend [LEGEND [LEGEND ...]]] [--nolegend]
[--nogrid]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --verbose increase verbose output
-s SILENT, --silent SILENT
show only fatal errors
--chan CHAN [CHAN ...]
One or more channel names.
--start START [START ...]
Starting GPS times(required)
--duration DURATION Duration (seconds) [10]
-c FRAMECACHE, --framecache FRAMECACHE
use .gwf files in cache not NDS2, default use NDS2
--highpass HIGHPASS frequency for high pass butterworth, default no filter
--secpfft SECPFFT length of fft in seconds for each calculation
--overlap OVERLAP Overlap as fraction [0-1)
--nologf make frequency axis linear, default=logarithmic
--fmin FMIN min value for frequency axis
--fmax FMAX max value for frequency axis
--nology make Y-axis linear, default=logarthmic
--ymin YMIN fix min value for yaxis defaults to min of data
--ymax YMAX max value for y-axis default to max of data
-g GEOMETRY, --geometry GEOMETRY
size of resulting image WxH, default: 1200x600
--interactive when running from ipython allows experimentation
--title TITLE One or more title lines
--suptitle SUPTITLE 1st title line (larger than the others)
--xlabel XLABEL x axis text
--ylabel YLABEL y axis text
--out OUT output filename, type=ext (png, pdf, jpg),
default=gwpy.png
--legend [LEGEND [LEGEND ...]]
strings to match data files
--nolegend do not display legend
--nogrid do not display grid lines
Next