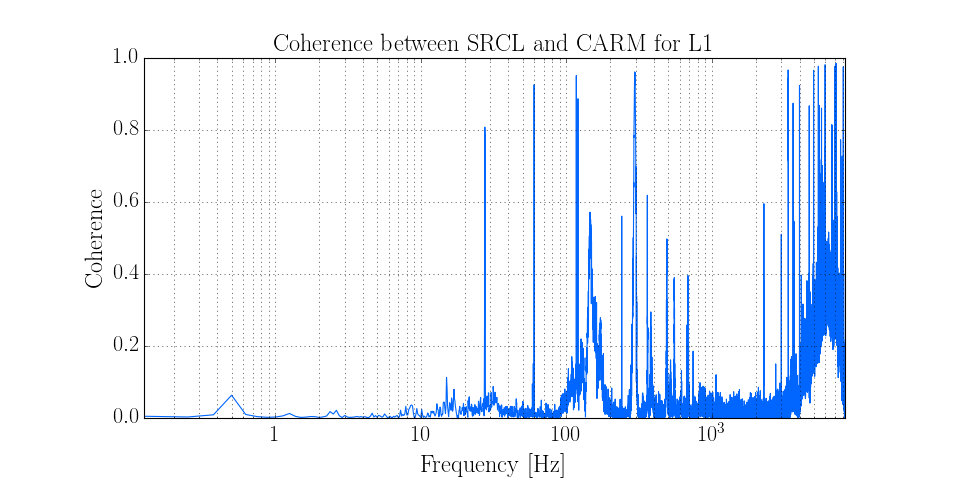
Calculating the coherence between two channels¶
The coherence between two channels is a measure of the frequency-domain correlation between their time-series data.
In LIGO, the coherence is a crucial indicator of how noise sources couple into the main differential arm-length readout.
In this example we calculate the coherence between two length-sensing degrees of freedom, the Signal-Recycling Cavity length (SRCL), and the Common-Arm motion (CARM).
First, we import the TimeSeriesDict
from gwpy.timeseries import TimeSeriesDict
and then get() both data sets:
data = TimeSeriesDict.get(['L1:LSC-SRCL_IN1_DQ', 'L1:LSC-CARM_IN1_DQ'],
'Feb 13 2015', 'Feb 13 2015 00:15')
We can then calculate the coherence() of one
TimeSeries with respect to the other, using an 8-second Fourier
transform length, with a 4-second (50%) overlap:
coh = data['L1:LSC-SRCL_IN1_DQ'].coherence(data['L1:LSC-CARM_IN1_DQ'], 8, 4)
Finally, we can plot() the resulting data:
plot = coh.plot(figsize=[12, 6], label=None)
ax = plot.gca()
ax.set_yscale('linear')
ax.set_xlabel('Frequency [Hz]')
ax.set_ylabel('Coherence')
ax.set_title('Coherence between SRCL and CARM for L1')
ax.grid(True, 'both', 'both')
plot.show()
(Source code, png)