Plotting time-domain data¶
Plotting one TimeSeries¶
The TimeSeries class includes a plot() method to
trivialise visualisation of the contained data.
Reproducing the example from Remote data access:
>>> l1hoft = TimeSeries.fetch_open_data('L1', 'Sep 14 2015 09:50:29', 'Sep 14 2015 09:51:01')
>>> plot = l1hoft.plot()
>>> plot.show()
(png)
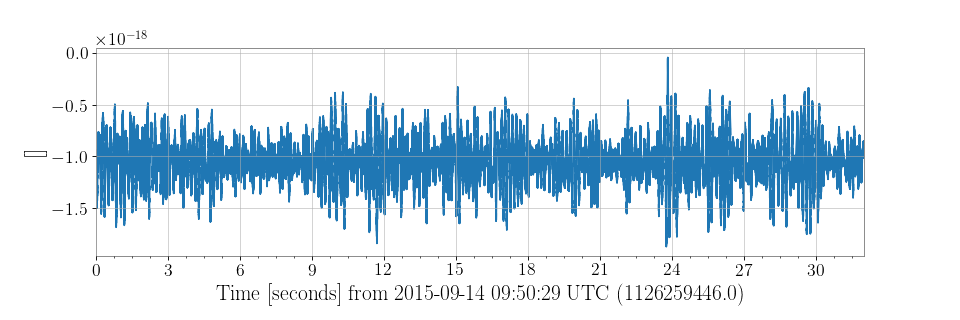
The returned object plot is a Plot, a sub-class of
matplotlib.figure.Figure adapted for GPS time-stamped data.
Customisations of the figure or the underlying Axes can
be done using standard matplotlib methods.
For example:
>>> ax = plot.gca()
>>> ax.set_ylabel('Gravitational-wave amplitude [strain]')
>>> ax.set_epoch(1126259462)
>>> ax.set_title('LIGO-Livingston strain data around GW150914')
>>> ax.axvline(1126259462, color='orange', linestyle='--')
>>> plot.refresh()
(png)
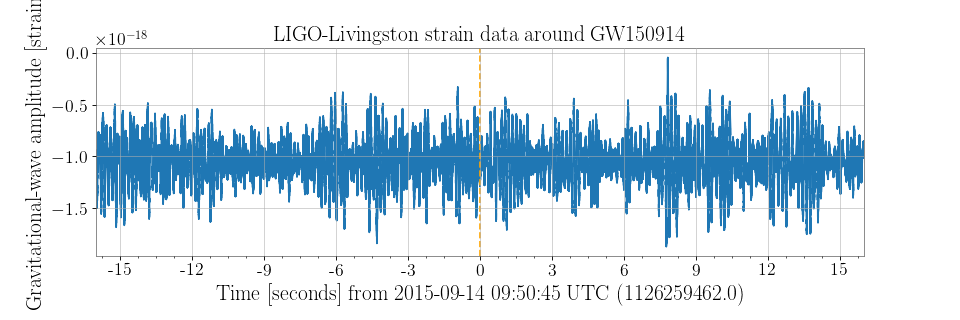
Here the set_epoch() method is used to reset the
reference time for the x-axis.
Plotting multiple TimeSeries together¶
Multiple TimeSeries classes can be combined on a figure in a number of
different ways, the most obvious is to plot() the first,
then add the second on the same axes.
Reusing the same plot from above:
>>> h1hoft = TimeSeries.fetch_open_data('H1', 'Sep 14 2015 09:50:29', 'Sep 14 2015 09:51:01')
>>> ax = plot.gca()
>>> ax.plot(h1hoft)
>>> plot.refresh()
(png)
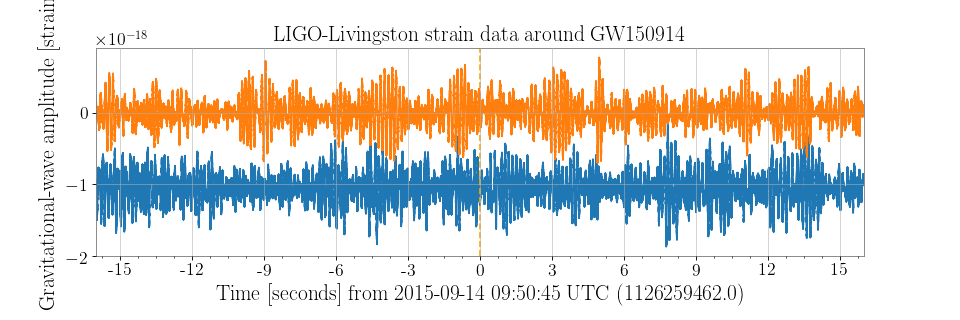
Alternatively, the two TimeSeries could be combined into a
TimeSeriesDict to use the plot() method from that class:
>>> combined = TimeSeriesDict()
>>> combined['L1'] = l1hoft
>>> combined['H1'] = h1hoft
>>> plot = combined.plot()
>>> plot.gca().legend()
>>> plot.show()
(png)
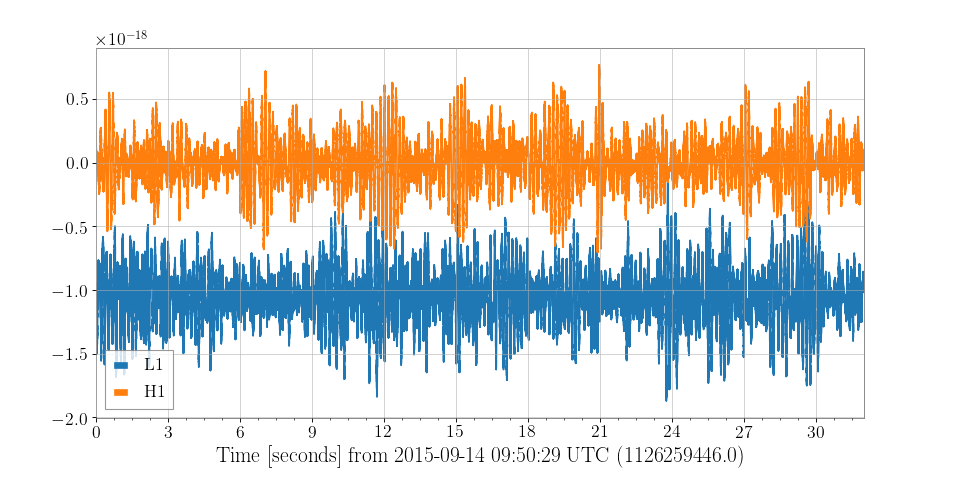
The third method of achieving the same result is by importing and accessing the Plot object directly:
>>> from gwpy.plot import Plot
>>> plot = Plot(l1hoft, h1hoft)
>>> plot.show()
(png)
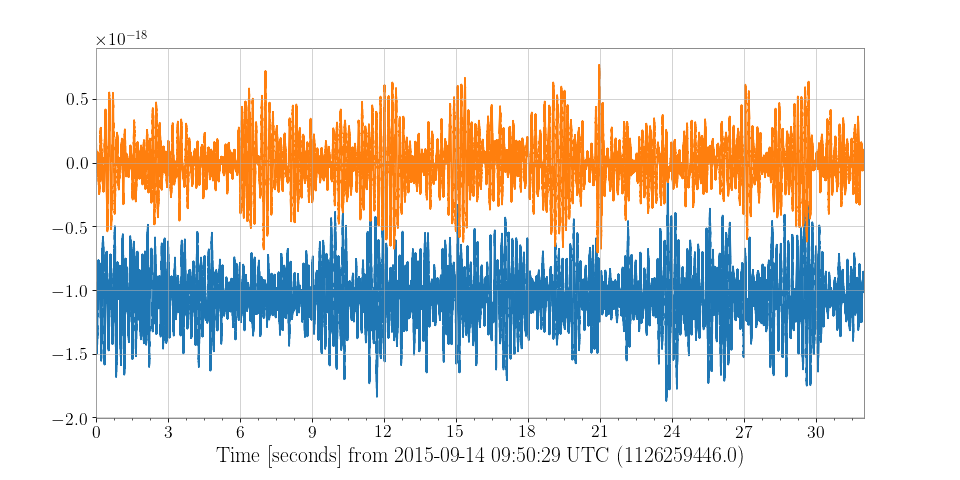
Using the Plot directly allows for greater customisation.
The separate=True keyword argument can be used to plot each TimeSeries
on its own axes, with sharex=True given to link the time scales for each
Axes:
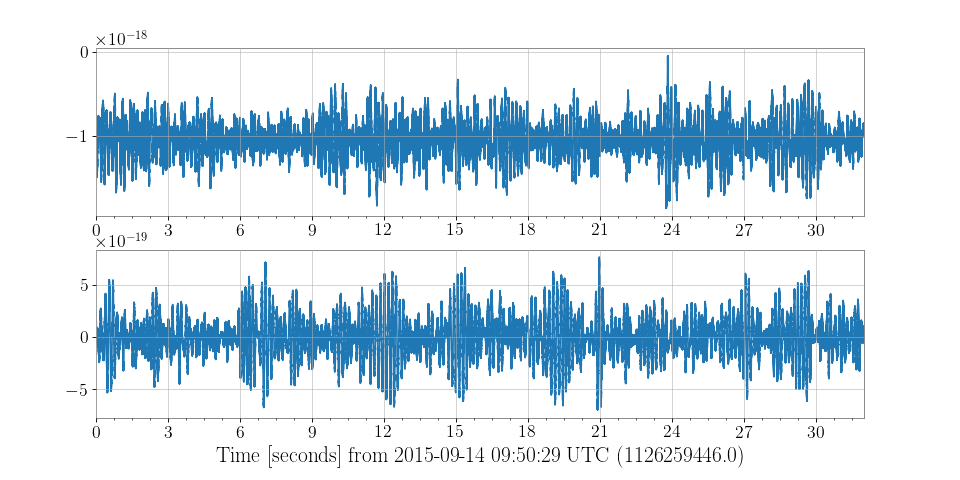
>>> plot = Plot(l1hoft, h1hoft, separate=True, sharex=True)
>>> plot.show()
(png)
Plotting a StateVector¶
A StateVector can be trivially plotted in two ways, specified by the
format keyword argument of the plot() method:
Format |
Description |
|---|---|
|
A bit-wise representation of each bit in the vector (default) |
|
A standard time-series representation |
>>> h1state = StateVector.fetch_open_data('H1', 'Sep 14 2015 09:50:29', 'Sep 14 2015 09:51:01')
>>> plot = h1state.plot(insetlabels=True)
>>> plot.show()
(png)
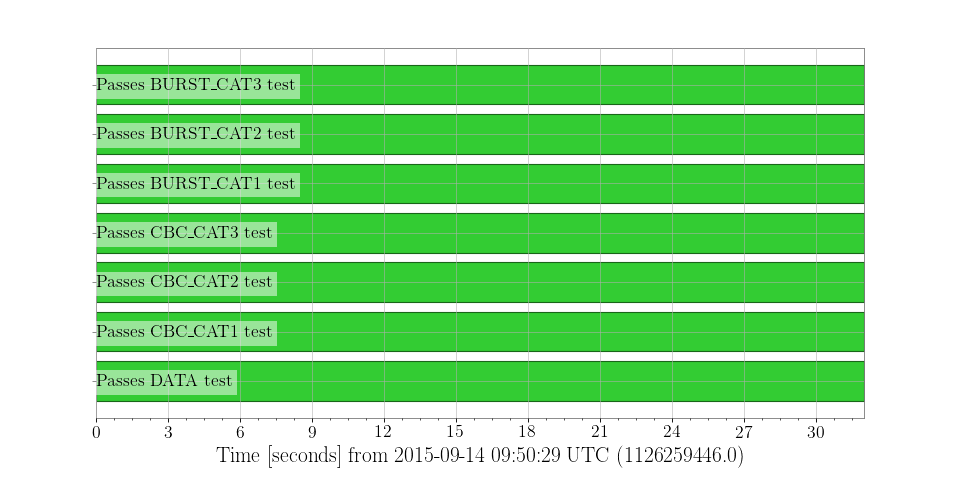
For a format='segments' display the bits attribute
of the StateVector is used to identify and label each of the binary bits
in the vector.
Also, the insetlabels=True keyword was given to display the bit labels
inside the axes (otherwise they would be cut off the side of the figure).
That each of the segment bars is green for the full 32-second duration
indicates that each of the statements (e.g. ‘passes cbc CAT1 test’) is
true throughout this time interval.