The Spectrogram¶
While the TimeSeries allows us to study how the amplitude of a signal changes over time, and the FrequencySeries allows us to study how that amplitude changes over frequency, the time-frequency Spectrogram allows us to track the evolution of the FrequencySeries over over time.
This object is a 2-dimensional array, essentially a stacked set of spectra, one per unit time.
As always, a Spectrogram can be generated from any abitrary data sequence, but here the required metadata are a combination of those required for the TimeSeries and FrequencySeries:
>>> import numpy
>>> specgram = Spectrogram(numpy.random.random((100, 1000)), epoch=1000000000, sample_rate=1, f0=0, df=1)
>>> print(specgram)
Spectrogram([[ 0.58030742 0.94586261 0.79559404 ..., 0.25253688 0.61626489
0.22785403]
[ 0.95930736 0.93154594 0.13234058 ..., 0.13920997 0.94432426
0.29442085]
[ 0.66572174 0.77702177 0.8900096 ..., 0.18828231 0.81440898
0.97455031]
...,
[ 0.46696636 0.72475187 0.17941277 ..., 0.19095158 0.83843501
0.92154324]
[ 0.81492468 0.01945053 0.77665596 ..., 0.73642962 0.78723728
0.20995951]
[ 0.35161785 0.79137264 0.50710421 ..., 0.39068193 0.61551753
0.74846848]],
name: None,
unit: None,
epoch: 2011-09-14 01:46:59.000,
dt: 1 s,
f0: 0 Hz,
df: 1 Hz,
logf: False)
The full set of metadata that can be provided is as follows:
name |
Name for this data set |
unit |
The physical unit of these data |
epoch |
Starting GPS epoch for this Spectrogram |
dt |
Time-spacing for this Spectrogram |
f0 |
Starting frequency for this Spectrogram |
df |
Frequency spacing of this Spectrogram |
Calculating a Spectrogram from a TimeSeries¶
The time-frequency Spectrogram of a TimeSeries can be calculated using the spectrogram().
We can extend previous examples of plotting a TimeSeries with calculation of a Spectrogram with a 20-second stride:
from gwpy.timeseries import TimeSeries
gwdata = TimeSeries.fetch('H1:LDAS-STRAIN', 'September 16 2010 06:40',
'September 16 2010 06:50')
specgram = gwdata.spectrogram(20, fftlength=8, overlap=4) ** (1/2.)
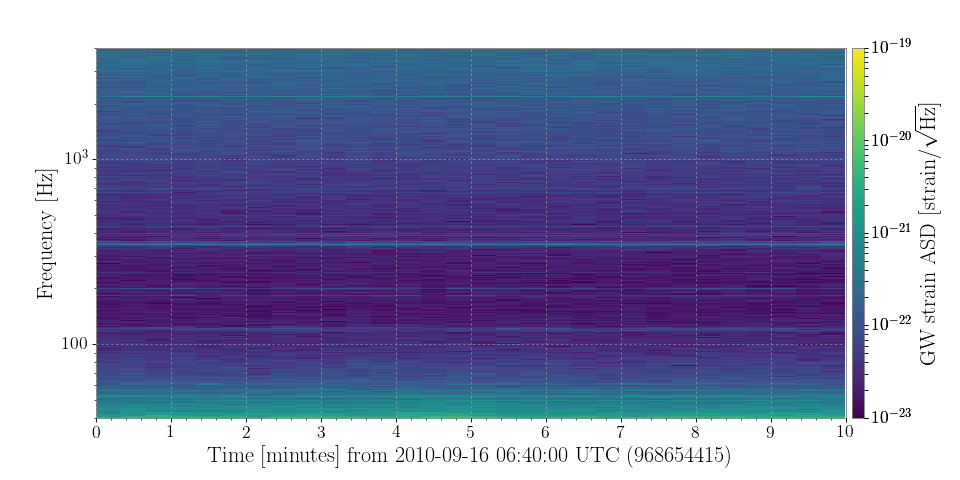
Plotting a Spectrogram¶
Like the TimeSeries and FrequencySeries, the Spectrogram has a convenient plot() method, allowing us to view the data.
We can extend the previous time-series example to include a plot:
from gwpy.timeseries import TimeSeries
gwdata = TimeSeries.fetch('H1:LDAS-STRAIN', 'September 16 2010 06:40',
'September 16 2010 06:50')
specgram = gwdata.spectrogram(20, fftlength=8, overlap=4) ** (1/2.)
plot = specgram.plot(norm='log', vmin=1e-23, vmax=1e-19)
ax = plot.gca()
ax.set_ylim(40, 4000)
ax.set_yscale('log')
plot.add_colorbar(label='GW strain ASD [strain/$\sqrt{\mathrm{Hz}}$]')
plot.show()
(png)
Spectrogram applications¶
Reference/API¶
Spectrogram |
A 2D array holding a spectrogram of time-frequency data |